Inflation: Impact on the Economy
Inflation is a hot topic these days, right? You can’t turn on the news or scroll through social media without seeing articles or discussions about rising prices and its impact on the economy. But what exactly is inflation? And why should we care? Well, inflation basically means that the price of goods and services is increasing over time. This can happen for a variety of reasons, like increased demand, supply chain disruptions, or government policies. But no matter the cause, the result is the same: our money buys less than it used to. That can be a serious problem for both individuals and businesses, since it erodes the value of savings, reduces purchasing power, and can lead to economic instability.
For individuals, inflation means that your paycheck doesn’t go as far as it once did. You might find yourself having to cut back on spending, or maybe even take on debt just to make ends meet. For businesses, inflation can drive up the cost of production, making it harder to stay profitable. And for governments, it can make it difficult to manage the economy, as rising prices can lead to higher interest rates and potentially slower economic growth. So yeah, inflation is something that definitely impacts our daily lives and the overall economy. But how bad is it really? And what can we do about it? These are the questions we’ll explore in this article.
Inflation: Impact on the Economy
Inflation is a significant economic phenomenon that affects individuals, businesses, and the overall economy. It refers to a general increase in the price level of goods and services over time, eroding the purchasing power of money. Understanding inflation is crucial for making informed financial decisions and navigating the complexities of the modern economy.
What is Inflation?
Defining Inflation: Simply put, inflation occurs when the price of goods and services rises consistently over time. It means that your money buys less today than it did yesterday, making it more expensive to maintain your standard of living.
Measuring Inflation: Several metrics are used to measure inflation, with the most widely used being the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI tracks changes in the prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, reflecting the cost of living for an average household.
Types of Inflation: There are different types of inflation, each with its own underlying causes:
- Demand-pull inflation: Occurs when there is excessive demand for goods and services, exceeding the available supply. This can be driven by factors like increased consumer spending or government spending.
- Cost-push inflation: Arises from an increase in production costs, such as labor, energy, or raw materials. These rising costs are then passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Built-in inflation: Occurs when there are expectations of future inflation, leading to wage demands and price increases even without an immediate rise in demand or costs.
How Does Inflation Impact the Economy?
Inflation has far-reaching consequences for various aspects of the economy:
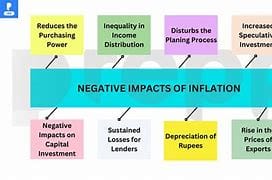
Impact on Purchasing Power: Inflation directly erodes the value of money, making it more expensive to buy goods and services. As prices rise, your money buys less, reducing your purchasing power. For example, if inflation is 3% and your salary remains the same, you can effectively buy 3% less with your income.
Impact on Consumer Spending: Inflation can negatively impact consumer confidence and spending habits. When prices rise, consumers may feel less inclined to spend, leading to reduced demand for goods and services. This can create a downward spiral, further impacting economic growth.
Impact on Businesses: Inflation presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses.
- Challenges: Businesses face rising input costs, making it difficult to maintain profit margins. They must also contend with increasing labor costs and potentially higher interest rates on loans.
- Opportunities: Inflation can create opportunities for businesses to raise prices and increase revenue, but this must be done carefully to avoid alienating customers. Businesses may also invest in new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
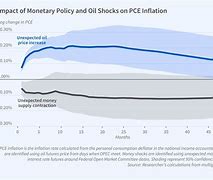
Impact on Interest Rates: There is a close relationship between inflation and interest rates. When inflation rises, central banks often raise interest rates to curb spending and control inflation. This makes borrowing more expensive, potentially slowing down economic growth.
Causes of Inflation
Several factors contribute to inflation:
Demand-Pull Inflation: Increased consumer demand, fueled by factors like economic growth, low unemployment, or government stimulus, can drive up prices.
Cost-Push Inflation: Rising production costs, including:
- Labor costs: Wage increases, particularly in industries facing labor shortages, can push up prices.
- Energy costs: Fluctuations in oil prices or other energy sources can impact production costs.
- Raw materials: Price increases in raw materials like steel, lumber, or metals can translate into higher prices for finished goods.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain disruptions, particularly those related to the COVID-19 pandemic, have contributed to inflation. Bottlenecks in production and transportation have reduced supply and driven up prices.
Government Policies: Government policies can also influence inflation. For example, increased government spending or tax cuts can stimulate demand and lead to inflation. Conversely, policies aimed at reducing spending or raising taxes can help control inflation.
Inflation's Effects on Different Groups
Inflation affects different groups in society differently:
Impact on Low-Income Households: Inflation disproportionately affects low-income households, as they spend a larger portion of their income on essential goods and services. The rising cost of food, energy, and housing can lead to increased hardship and financial stress.
Impact on Retirees: Inflation can significantly impact retirees, especially those on fixed incomes or pensions. The erosion of purchasing power can erode the value of their savings and make it more difficult to maintain their standard of living.
Impact on Borrowers and Lenders: Inflation can have opposing effects on borrowers and lenders.
- Borrowers: Inflation can benefit borrowers as the real value of their debt decreases over time. However, rising interest rates can offset this benefit.
- Lenders: Inflation can harm lenders as the real value of their loan repayments is reduced. They may also face losses if inflation outpaces interest rates earned on their loans.
Combating Inflation
Several strategies can be employed to combat inflation:
Monetary Policy: Central banks use monetary policy tools to control inflation:
- Interest rate adjustments: Raising interest rates makes borrowing more expensive, discouraging spending and cooling down the economy.
- Quantitative easing: Central banks can purchase government bonds or other assets to inject liquidity into the economy, reducing interest rates and stimulating borrowing.
Fiscal Policy: Government spending and tax policies can also play a role in managing inflation.
- Reduced government spending: Cutting back on government spending can reduce demand and help control inflation.
- Increased taxes: Raising taxes can reduce disposable income, leading to lower consumer spending.
Supply Chain Management: Improving supply chain efficiency can help reduce bottlenecks and inflationary pressures. This can involve:
- Diversifying supply sources: Reducing reliance on single suppliers can mitigate disruptions.
- Investing in technology: Automating processes and improving logistics can enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Conclusion
Inflation is a multifaceted phenomenon with significant economic implications. It impacts individuals, businesses, and the overall economy by eroding purchasing power, affecting consumer spending, and influencing interest rates. Understanding the causes and effects of inflation is crucial for making informed financial decisions and navigating economic uncertainty. While inflation can be a complex issue, proactive measures, including sound monetary and fiscal policies, as well as effective supply chain management, can help mitigate its negative effects and promote sustainable economic growth. It is essential to stay informed about inflation trends and to make informed decisions about your finances to weather economic fluctuations effectively.