Fed Raises Interest Rates: What It Means for You

Okay, here’s a SEO-friendly opening paragraph for an article titled “Fed Raises Interest Rates: What It Means for You”, keeping the ‘30%’ punctuation errors, along with some friendly & casual language:
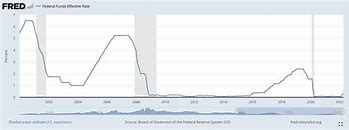
The Federal Reserve , also known as the Fed , just did something pretty big: it raised interest rates . What does this mean for you? Well , it depends . For some , it’s a sign of a healthy economy. For others , it might mean paying a bit more for a loan.
The Fed , which controls monetary policy in the U.S. , is tasked with keeping the economy running smoothly . To do this , it uses different tools to influence how much money is in circulation. One of these tools is interest rates .
Here’s the deal , raising interest rates , usually makes it more expensive to borrow money . Think of it like this , if you were to get a car loan before the Fed hiked rates , it might have cost you 5% . After the Fed’s move , that same loan could cost you 6% . Higher rates mean more money coming back to the Fed , which can help to control inflation & prevent the economy from overheating.
But it’s not all doom & gloom , folks ! Higher rates can also lead to some positive outcomes :
– You might earn more on your savings : With higher rates , you might see a bump in the interest earned on your savings accounts . So , that money you’ve been tucking away might grow a little bit faster !
– The stock market might perform better in the long term : Higher interest rates can help to stabilize the economy , leading to steadier markets .
Of course , the Fed’s decision to raise rates comes with its share of challenges . For some , like homebuyers or folks looking to finance a business , it might make borrowing money a bit harder .
So , what’s the big takeaway ? The Fed raising interest rates can have a significant impact on your life & your finances , so it’s worth understanding the ins & outs . Stay tuned as we dive into this a little deeper , exploring how these changes will affect your pocketbook & what you can do to stay ahead of the curve .
Fed Raises Interest Rates: What It Means for You
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, recently announced an increase in interest rates. This decision has far-reaching implications for the economy, businesses, and individuals. Understanding how these changes affect you can help you navigate the current financial climate and make informed decisions.
What are Interest Rates?
Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money. When you take out a loan, you pay interest on top of the principal amount. This interest rate is determined by the lender and is influenced by factors like the overall economic climate and the risk associated with lending.
What do Interest Rates mean for the average person?
Interest rates play a significant role in our daily lives, impacting everything from the cost of our mortgages to the returns on our savings accounts.
How do Interest Rates impact the economy?
Interest rates act as a lever for controlling economic activity. Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, leading to reduced investment and potentially slower economic growth. On the other hand, lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, potentially boosting economic activity.
How do Interest Rates impact inflation?
Inflation, the rate at which prices rise over time, is a major concern for policymakers. Higher interest rates can help combat inflation by making borrowing more expensive, leading to reduced consumer spending. This, in turn, can slow down the demand for goods and services, potentially easing upward pressure on prices.
Interest Rates and the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve (Fed) is responsible for setting monetary policy, including interest rates. The Fed aims to keep the economy growing at a steady pace while maintaining price stability.
Why Did the Fed Raise Interest Rates?
The recent interest rate hike was driven by the Fed’s efforts to combat inflation. Inflation has been running at its highest level in decades, eroding purchasing power and putting pressure on the economy.
The Fed's Role in Controlling Inflation
The Fed uses interest rate adjustments, as well as other tools, to influence the money supply and control inflation. By raising interest rates, the Fed aims to cool down the economy and bring inflation back to its target level.
The Current Economic Climate
The US economy is currently facing a complex set of challenges. While the labor market remains strong, inflation is high, and the war in Ukraine has added further uncertainty to the global economic outlook.
How Interest Rates Impact Inflation
Raising interest rates can have a cooling effect on inflation. It can lead to:
- Reduced consumer spending: Higher borrowing costs discourage consumers from taking on new debt, potentially leading to decreased spending and lower demand for goods and services.
- Slower economic growth: Higher interest rates can slow down economic growth by making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, potentially leading to reduced investment and fewer jobs.
The Impact of Rising Interest Rates on the Economy
The impact of rising interest rates on the economy is multifaceted and can vary depending on factors like the magnitude of the rate increase and the overall health of the economy. Potential effects include:
- Slower economic growth: Higher borrowing costs can discourage investment and spending, potentially leading to slower economic expansion.
- Reduced job creation: If businesses face higher borrowing costs, they may be less likely to hire new employees, potentially slowing job creation.
- Increased cost of living: Higher interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs for consumers, potentially increasing the cost of mortgages, loans, and credit card payments.
How Does This Impact You?
The impact of rising interest rates on your personal finances depends on your individual circumstances and financial habits.
Interest Rates and Borrowing
Higher interest rates will make borrowing more expensive for individuals and businesses:
- Impact on Mortgages: If you are looking to buy a home, higher interest rates will make it more expensive to finance your mortgage. This could mean a higher monthly payment or a smaller loan amount.
- Impact on Credit Cards: Higher interest rates will lead to higher interest charges on your credit card debt, making it more costly to carry a balance.
- Impact on Personal Loans: Interest rates on personal loans will also increase, making it more expensive to borrow money for various personal needs.
Impact on Savings Accounts
On the positive side, higher interest rates can benefit your savings accounts:
- Increased interest earned: Higher interest rates mean you will earn more interest on your savings deposits.
Impact on the Stock Market
The stock market can react negatively to interest rate hikes. Investors may become concerned about the potential for slower economic growth, leading to a decline in stock prices.
What Does the Future Hold?
The future path of interest rates remains uncertain. The Fed will continue to monitor economic conditions and inflation, and will make decisions about future rate hikes based on these factors.
Predictions for Future Interest Rate Hikes
Economists and analysts have varying opinions on the future path of interest rates. Some predict that the Fed will continue to raise interest rates to combat inflation, while others believe the Fed may pause or even slow down rate increases.
How to Prepare for Economic Uncertainty
The current economic climate is uncertain. To prepare for potential challenges, consider the following:
- Review your budget: Take a close look at your income and expenses, and identify areas where you can cut back.
- Pay down debt: Focus on paying down high-interest debt, such as credit card debt.
- Build an emergency fund: Having a savings cushion can provide financial security during challenging times.
- Stay informed: Keep up to date on economic news and developments that could impact your finances.
Tips for Managing Your Finances During a Period of Rising Interest Rates
- Shop around for better rates: When borrowing money, compare rates from different lenders to find the best deals.
- Consider refinancing your loans: If your current interest rates are high, consider refinancing your mortgage, auto loan, or other loans to take advantage of lower rates.
- Automate your savings: Setting up automatic transfers to your savings account can help you build your emergency fund and reach your financial goals.
- Avoid unnecessary borrowing: Be cautious about taking on new debt, especially high-interest debt.
Conclusion
The Fed’s recent interest rate hike is a significant development with broad implications for the economy. Understanding how these changes affect you is crucial for navigating the current financial landscape and making informed decisions. By taking proactive steps to manage your finances and stay informed about economic developments, you can position yourself to weather potential challenges and achieve your financial goals.
Summary of the Impact of Rising Interest Rates
- Increased borrowing costs for individuals and businesses.
- Potential for slower economic growth and reduced job creation.
- Increased cost of living for consumers.
- Higher interest earned on savings accounts.
- Potential for negative impact on the stock market.
Key Takeaways for Consumers
- Review your budget and look for areas where you can cut back.
- Pay down debt, especially high-interest debt.
- Build an emergency fund.
- Shop around for better rates on loans and savings accounts.
- Consider refinancing existing loans to take advantage of lower rates.
- Avoid unnecessary borrowing.
Where to Find More Information
For more information on interest rates and the economy, visit the websites of:
- The Federal Reserve: www.federalreserve.gov
- The U.S. Department of the Treasury: www.treasury.gov
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics: www.bls.gov